The revised EU GMP Annex 1 is intended to provide comprehensive guidance to manufacturers of sterile products. Changes include the design and control of facilities, equipment, systems, and procedures ensuring that microbial, particulate and endotoxin/pyrogen contamination are prevented.
It's important to note - not only are these new regulations beneficial for manufacturing sterile products, but for any products where the control and reduction of microbial, particulate and endotoxin/pyrogen contamination are important.
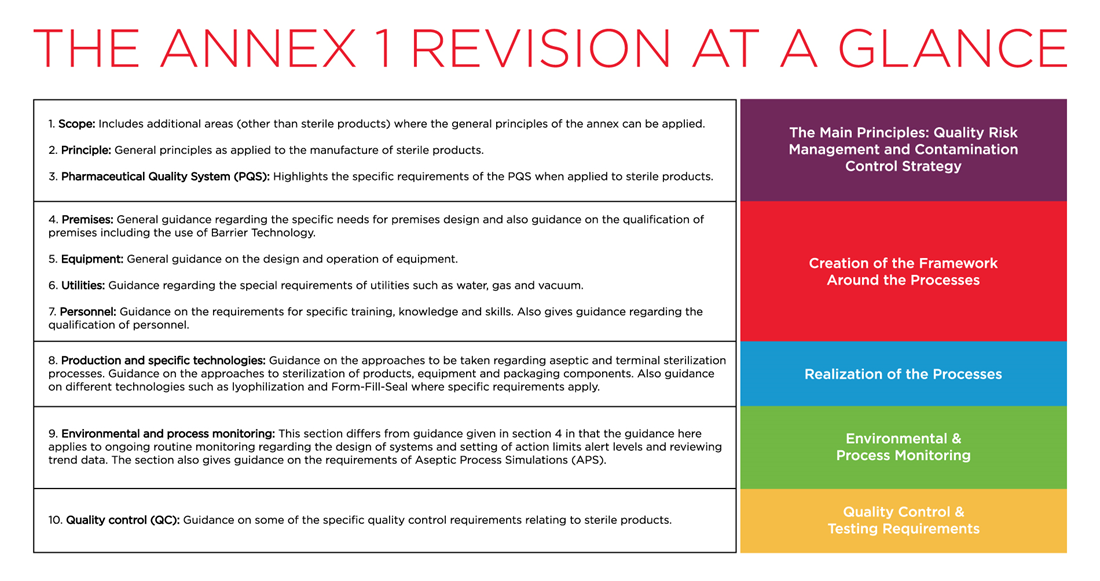
A Contamination Control Strategy is Key
The revised Annex 1 emphasizes the importance of applying the principles of Quality Risk Management (QRM), ensuring continuous environmental monitoring and the development of a robust Contamination Control Strategy (CCS). With this important addition, we see a more holistic approach to creating quality, safe, contaminant-free products.
CCS is defined as “a planned set of controls for microorganisms, endotoxin/pyrogen and particles, derived from current product and process understanding that ensures process performance and product quality. The controls can include parameters and attributes related to active substance, excipient and drug product materials and components, facility and equipment operating conditions, in-process controls, finished product specifications, and the associated methods and frequency of monitoring and control.”
Water System and Environmental Monitoring - What You Need to Know
The qualification/classification of water systems, cleanroom and environmental monitoring is extremely important.
Our solutions for analyzing total organic carbon, environmental monitoring and particle counting are used every day to help ensure quality and safety in diverse applications. In fact, we share a name with measurement principles that drive particle counting and characterization technology (i.e., the Coulter and HIAC principles) and are a trusted resource for instruments that deliver critical data to researchers, formulation development scientists and GMP-regulated quality control departments around the world.
Water Systems and the Revised EU GMP Annex 1
The revised EU GMP Annex 1 specifies the requirements of utilities, including water. Two parts that stand out are 6.14 and 6.15.
- Section 6.14 states:
- Alert level excursions should be documented and reviewed, and include an investigation to determine whether the excursion is a single (isolated) event or if results are indicative of an adverse trend or system deterioration. Each action limit excursion should be investigated to determine the probable root causes and any potential impact on the quality of products and manufacturing processes as a result of the use of the water.
-
Section 6.15 states:
- Water for injections (WFI) systems should include continuous monitoring systems such as Total Organic Carbon (TOC) and conductivity, as these may give a better indication of overall system performance than discrete sampling. Sensor locations should be based on risk.
How the ANATEL PAT700 TOC Analyzer Can Help You Comply
The ANATEL PAT700 TOC analyzer is specifically designed to help demonstrate compliance to the pharmacopoeia requirements for TOC and conductivity for purified water and WFI systems.
- TOC, conductivity and water temperature data from a single instrument
- Excursion capture feature enables a water sample to be captured to assist root cause analysis if a TOC excursion is detected
- Built-in grab-sample analyzer for analyzing samples from other points in the water loop
Environmental Monitoring and the Revised EU GMP Annex 1
Sections 4 and 9 of the revised EU GMP Annex 1 provides guidance regarding the specific needs for premises design, the ongoing routine monitoring related to the design of systems, and setting of action limits alert levels and reviewing trend data.
- Section 4.28 states:
- For classification of the cleanroom, the minimum number of sampling locations and their positioning can be found in ISO 14644 Part 1. For the aseptic processing area and the background environment (the grade A and grade B areas, respectively), additional sample locations should be considered and all critical processing areas such as the point of fill and container closure feeder bowls should be evaluated. Critical processing locations should be determined by documented risk assessment and knowledge of the process and operations to be performed in the area.
- For classification of the cleanroom, the minimum number of sampling locations and their positioning can be found in ISO 14644 Part 1. For the aseptic processing area and the background environment (the grade A and grade B areas, respectively), additional sample locations should be considered and all critical processing areas such as the point of fill and container closure feeder bowls should be evaluated. Critical processing locations should be determined by documented risk assessment and knowledge of the process and operations to be performed in the area.
-
Section 9.4 states:
-
An environmental monitoring program should be established and documented. The purpose of the environmental monitoring program is to:
- Provide assurance that cleanrooms and clean air equipment continue to provide an environment of appropriate air cleanliness, in accordance with design and regulatory requirements.
- Effectively detects excursions from environmental limits triggering investigation and assessment of risk to product quality.
-
How MET ONE Air Particle Counters Can Help You Comply
MET ONE air particle counters enable you to monitor air cleanliness in compliance with ISO 14644, FDA CGMP and EU GMP Annex 1.
MET ONE 3400+ Series Portable Airborne Particle Counter
The MET ONE 3400+ Series portable airborne particle counter features automated, integrated electronic SOPs and sampling maps.
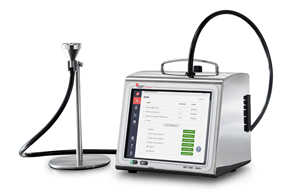
- Plug-and-play networking—connected instruments automatically create a network
- Customized, electronic SOP maps—using a web-browser interface, load your SOP map into the counter, mark sample locations, and define SOP requirements for each
- Up to 26% lighter than previous models—a mere 12.4 lbs (5.6 kg) without batteries
Facility Monitoring Systems (FMS)

By pairing MET ONE air particle counters, you get custom workflow-optimized solutions for monitoring complex production methods across several production lines.
Each instrument is built around proven MET ONE technology, including the portable MET ONE 3400 Series for routine monitoring and cleanroom classification as well as the 6000 and 7000 Series of fixed, non-viable air particle counters.
Discover How Our Solutions Can Help You Comply With EU GMP Annex 1
Let's Get Started
Whether you have questions or are ready to order, we're here to help.
What can we do for you today?






