Biomek i-Series Automation of the DNAdvance Genomic DNA Isolation Kit
Biomek Automated Genomic Sample Prep Accelerates ResearchIntroduction
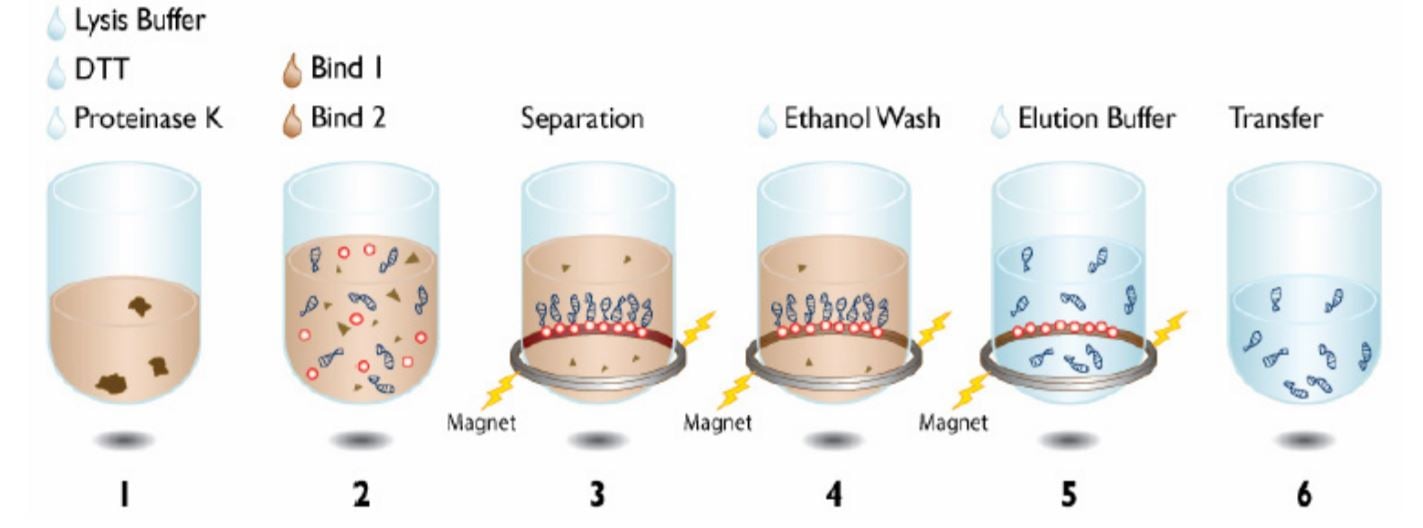
The Agencourt DNAdvance DNA isolation kit uses Beckman Coulter’s patented Agencourt SPRI paramagnetic beadbased technology to isolate genomic DNA from a variety of sources. The extraction process begins by rupturing cell membranes and digesting protein with lysis buffer, DTT, and Proteinase K (Figure 1). Thereafter, binding buffer is added to bind DNA on magnetic particles. The immobilization of DNA on magnetic particles allows rinsing away contaminations by washing. In addition, it enables automation of the procedure, as it eliminates the need for vacuum filtration or centrifugation. In this technical note, we demonstrate automated performance of DNAdvance Tissue Kit on Biomeck i series.
When compared to manual operations, The Agencourt DNAdvance Genomic DNA isolation kit automated on the Biomek platform provides:
- Reduced hands-on-time and increased throughput - Option to run the method end-to-end with only setup and tear-down touch points
- Reduction in pipetting errors
- Standardized workflow for improved results
- Quick implementation with demonstrated methods
- Knowledgeable support for reagents, automation and methods all from a single vendor
Figure 1. Beckman Coulter Agencourt DNAdvance Kit protocol
Automated method
The Biomek i series genomics workstations enable to extract DNA from 96 samples in less than 1 hour (Table 1). The i7 high throughput full plate method can process up to 5 plates at a time (Table 1). The data for this technical note has been collected using 1-96 sample method.
| Method | 1-96 samples¥ | 5 full plates◆ |
| Reagent and instrument preparation * | 15 mins | 15 mins |
| Agencourt DNAdvance Tissue method | 37 mins | 2 hrs |
| Total | 52 mins | 2 hrs and 15 mins |
* : Timing does not include reagent thawing, dissection, tissue lysis and homogenization
¥ : i5/i7 Multichannel method that uses Enhanced Selective Tip Pipetting for partial plates.
◆ : i7 Multichannel full plate method. Note: A 10 full plate method is also available with Integrated Devices.
Table 1. Estimated run times for Agencourt DNAdvance protocol on the Biomek i7 hybrid Genomics Workstation.
Demonstrated Method Interface (DMI)
The automated Agencourt DNAdvance protocol was implemented through a method interphase that provided the user full instructions to setup the method. It consisted of three modules.
1. Biomek Method Launcher (BML)
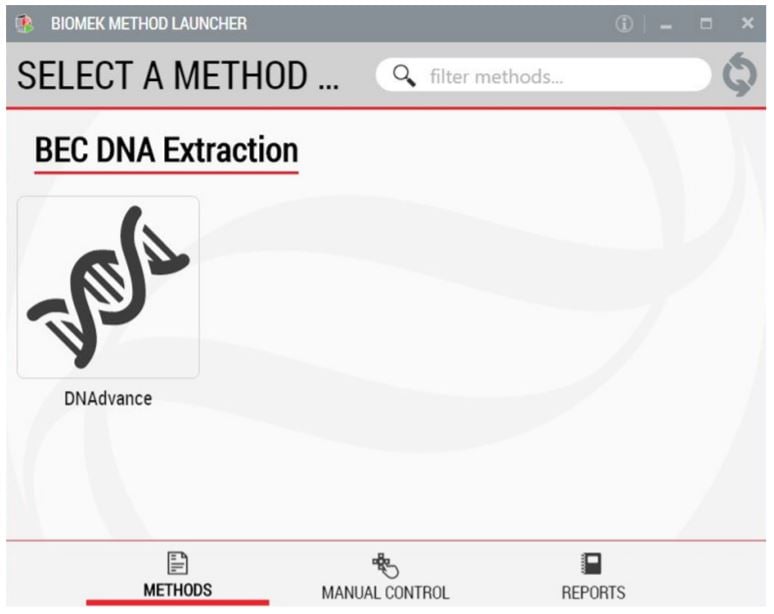
BML is a secure interface for selecting methods to run, without affecting method integrity (Figure 2). It allows the users to remotely monitor the progress of the run. The manual control options provide the opportunity to interfere if needed.
Figure 2. Biomek Method Launcher provides an easy interface to start the method
2. Method Options Selector (MOS)
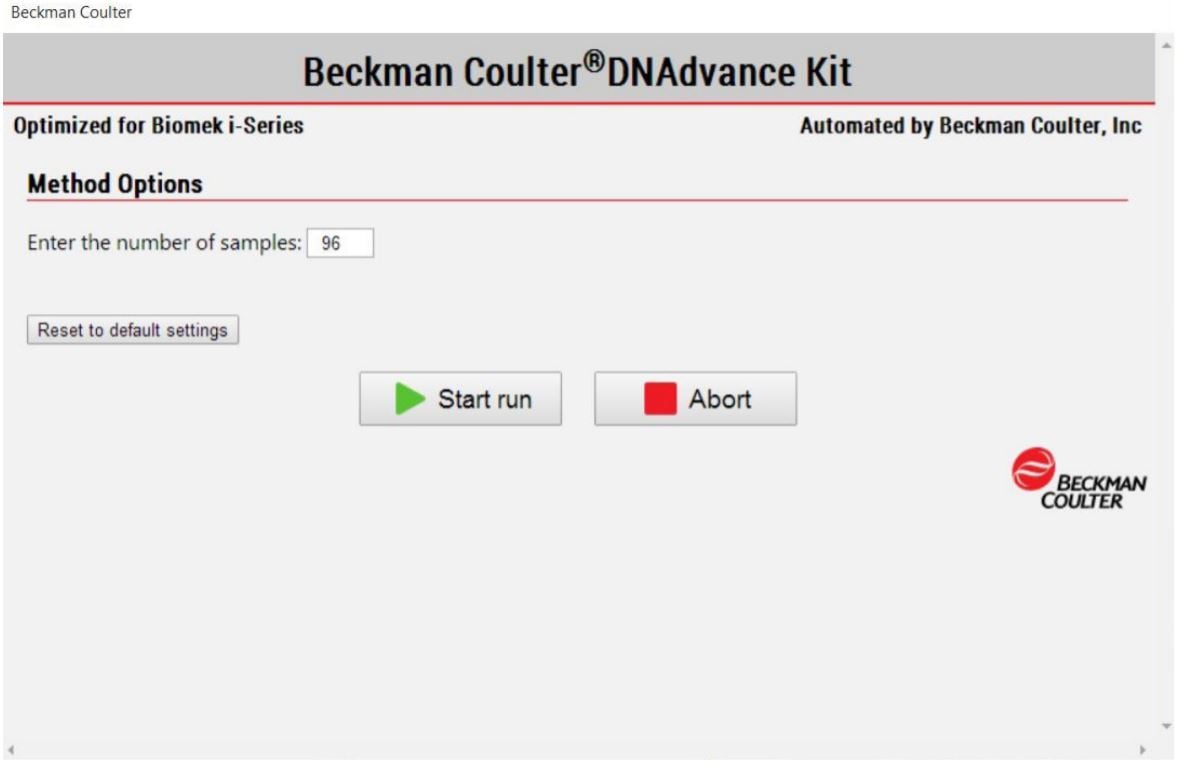
MOS enables selection of sample number to suit the needs of the user (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Biomek Method Options Selector indicates sample number and processing options
3. Guided Labware Setup (GLS)
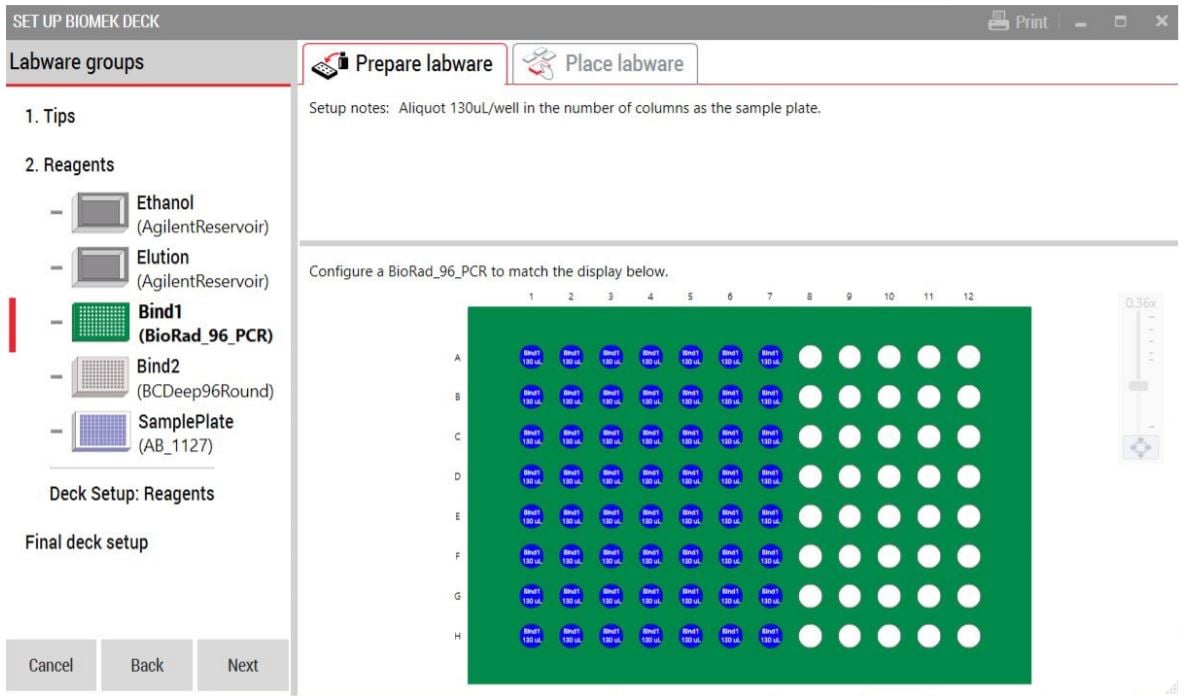
GLS is generated based on options selected in the MOS, and provides the user specific text and graphical setup instructions with reagent volume calculation and step by step instructions to prepare reagents (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Guided Labware Setup indicates reagent volumes and guides the user for correct deck setup
Experimental design
Approximately 10 mg of tissues each were excised from frozen mouse livers. DNA was extracted using both manual and automated DNAdvance protocol (4 replicates each). The quantity and the quality of the DNA samples were assessed using NanoDrop 2000TM (Thermo Fisher Scientific), Agilent TapeStation 2200 (with Agilent High Sensitivity D5000 ScreenTape system) and qPCR (KAPA SYBR® Fast One-Step qPCR Master Mix (2x), ACTB primer, reactions done in triplicates).
Results
Both manual and automated samples yielded good A260/A280 ratios (1.8–2.2) and acceptable A260/A230 ratios (>1.7 in general; Table 2).
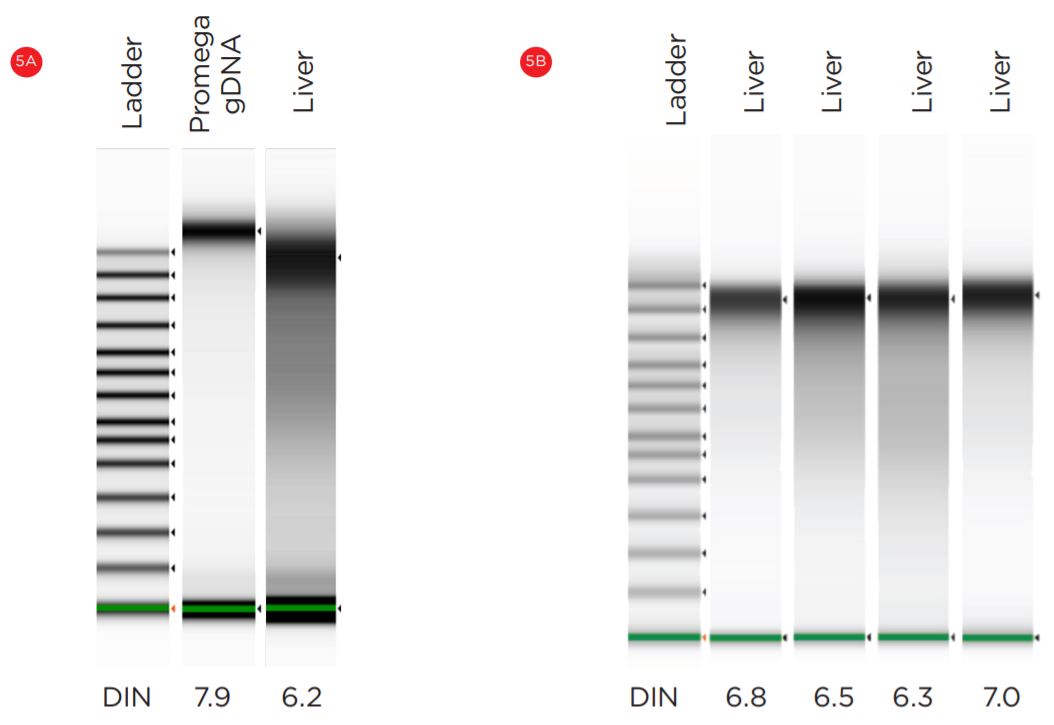
The DNA Integrity Numbers (DIN) calculated by tape station provided an estimate of DNA quality. Both manual and automated methods produced excellent DIN scores (Figure 5).
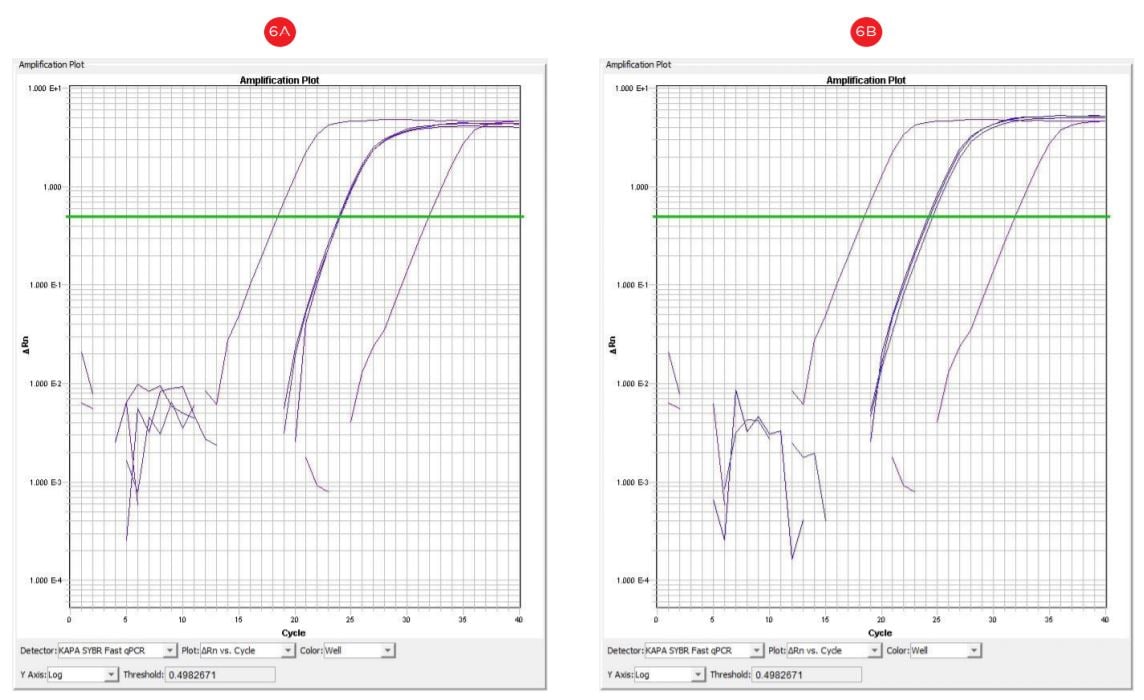
DNA extracted by both methods amplified in the range of Ct 20-25, indicating the usability for downstream application (Figure 6). Overall, the quality and the quantity of automated samples was comparable to the manual samples.
| Method | Tissue | NanoDrop | ||
| Concentration (ng/µL) | 260/280 | 260/230 | ||
| Manual | Liver | 129 | 1.86 | 1.6 |
| Manual | Liver | 114.8 | 1.82 | 2.02 |
| Manual | Liver | 146.7 | 1.96 | 1.43 |
| Manual | Liver | 207.6 | 1.89 | 1.61 |
| Automated | Liver | 130.5 | 1.85 | 1.96 |
| Automated | Liver | 214.7 | 1.93 | 1.97 |
| Automated | Liver | 146.9 | 1.94 | 1.81 |
| Automated | Liver | 119.9 | 1.84 | 2.04 |
Table 2. The concentration, yield and the purity of DNA as indicated by NanoDrop 2000
Figure 5. Manual (A) and automated (B) mouse DNA samples were analyzed on Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100.
Figure 6. qRT-PCR amplification plots (cycle number vs. florescence) corresponding to manual (A) and automated (B) DNA templates. DNA template concentration 100 ng; X: positive control DNA, 1 µg; y: no template control.
Summary
We have demonstrated automation of Agencourt DNAdvance protocol on the Biomek i5/i7 Multichannel Genomics Workstations. The quality and quantity of DNA extracted by the automated protocol was comparable to manually extracted DNA. Biomek Method Launcher provided a convenient interface for the customer to run the method, without affecting the method integrity.