CD300a (IRp60) Antibodies
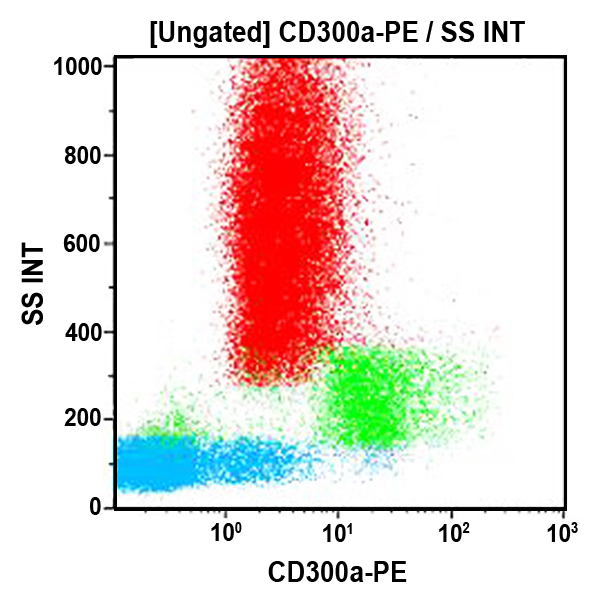
The CD300a, also known as inhibitory receptor protein (IRp60), is a surface molecule of 60 kDa expressed by all human natural killer (NK) cells. The IRp60 gene, located on human chromosome region 17q25 encodes a molecule, highly O- and N-glycosylated, belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily (Ig-SF) that displays one extracellular Ig‑like domain of the V-type, a hydrophobic transmembrane portion and a cytoplasmic tail containing ITIM motifs involved in the inhibitory function. The ligand of the CD300a is still unknown but CD300a does not appear to recognize HLA-class I molecules. Upon cross-linking, IRp60 recruits and activates SH2-containing phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 which switch off the activating signaling cascade by dephosphorylating a variety of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins. Cross‑linking of IRp60 by E59.126 monoclonal antibody strongly inhibits the spontaneous cytotoxicity of NK cells as well as the NK-mediated cytolytic activity induced via different non-HLA-specific or HLA-specific activating receptors. CD300a may play a more general role in the regulation of the immune response since it is expressed on other cell types, including T lymphocyte subsets, monocytes and granulocytes.
| Clone: E59.126 | Isotype: IgG1 Mouse |
| The E59.126 antibody has been used in flow cytometry and Western blotting to characterize IRp60. | |