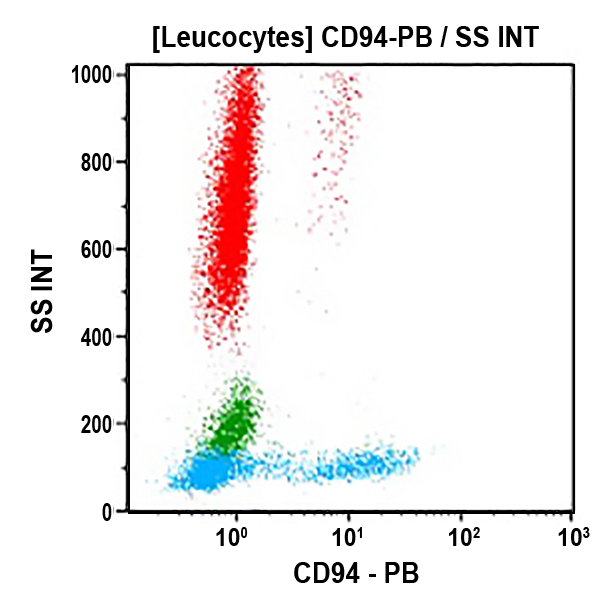
CD94 Antibodies
CD94 is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein of 30 kDa, belonging to the Ca2+-dependent (C-type) lectin family. Like NKG2A (or Kp43) on human natural killer (NK) cells, CD94 associates with one member of the NKG2 family to form disulphide-linked, NK cell receptor for MHC class I molecules, with a broader specificity than the human killer cell inhibitory (KIR) / activator (KAR) receptors of the Ig-superfamily. Ligation of CD94 either potently triggers or inhibits NK cell proliferation and cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Recent studies strongly indicate that the specificity of CD94/NKG2 receptors is for HLA-E, a non-classical MHC class I molecule. CD94/NKG2A and CD94/NKG2B heterodimers constitute inhibitory NK cell receptors, whereas the association of CD94 with NKG2C corresponds to an activating receptor. The expression of CD94 appears restricted to most NK cells and to a T lymphocyte subpopulation including a subset of γδ TCR+ T-cells and αβ TCR+ CD8+ CD56+ T-cells, mainly Vα2/Vδ2.
| Clone: HP-3B1 | Isotype: IgG2a Mouse |
| Ligation of CD94 with the HP-3B1 monoclonal antibody inhibits IL-2-dependent proliferation of NK-cells, and induces apoptosis in a subset of IL-2-stimulated NK cells. | |