Antibody Characterization with Analytical Ultracentrifugation
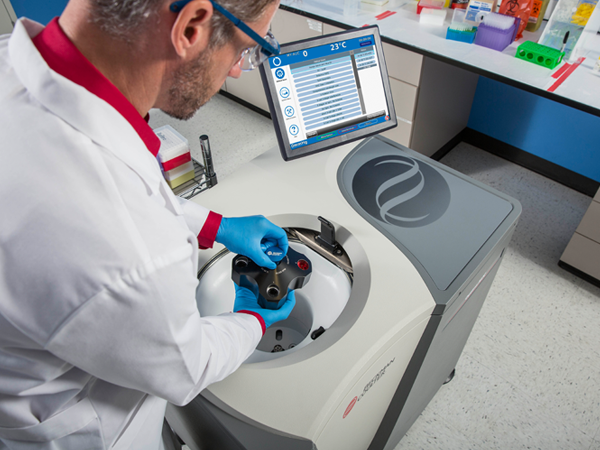
Clinical evaluation and manufacturing of protein therapeutics require rigorous characterization to ensure quality, safety, and efficacy. Analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) is a critical tool in this context, providing detailed insights into macromolecular integrity, heterogeneity, aggregation states, and interactions critical to therapeutic function. Its ability to directly measure sedimentation and diffusion properties under conditions similar to the formulated drug product without relying on matrix interference, and its capacity to characterize a wide range of therapeutics through centrifugal speed modulation, makes it uniquely advantageous. We also offer straightforward plate-based assays to determine IgG titer or protein aggregation through our Valita products.
In the biopharmaceutical sector, the method is particularly esteemed for its precision and reliability in analyzing monoclonal antibody-based formulations. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes AUC as a gold standard for determining molecular integrity, thereby supporting regulatory compliance and advancing therapeutic development pipelines.1
Sedimentation Velocity in AUC
Beyond monoclonal antibodies, AUC is extensively employed for characterizing diverse protein therapeutics, elucidating protein-ligand binding dynamics, monitoring self-association, oligomerization, and aggregation.1-3 Its applications span from early-stage research and preclinical studies to later stages of clinical evaluation and large-scale manufacturing, ensuring that therapeutic proteins meet stringent regulatory standards. AUC overcomes the limitations faced by using size exclusion chromatography (SEC), including on-column sample dilution, mobile phase incompatibility, stationary phase interactions, and restricted separation range, all of which lead to inaccurate aggregate characterization.2

Figure 1: Sedimentation velocity AUC simulated experiment of IgG measured at 42,000 RPM with a sedimentation coefficient of 6.6 S.
Sedimentation velocity (SV) experiments performed using AUC subject the antibody drug to centrifugal forces and separate the analytes in solutions based on their size and mass. Throughout the experiment, a light source is used to detect the sample sedimentation pattern, which provides high-resolution quantitative size distributions, protein interactions, and information on the analytes' conformation. Advances in computational methodologies have further enhanced the utility of SV, establishing it as the preferred approach for AUC applications, including the study of protein association, membrane protein analysis and various biotechnology applications.
Through the analysis of AUC results the following attributes can be determined:
- Size & Shape
Determine the size and shape of antibody drug molecules. - Aggregate Detection
Analyze aggregates in antibody drugs. -
Stability Insights
Assess antibody unfolding or denaturation via sedimentation coefficients to evaluate stability. -
Binding Efficiency
Characterize antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) binding efficiency, identifying bound and unbound ADCs.4 - Interaction Detection
Detect antigen-antibody interactions. - Batch Consistency
Perform batch consistency assays.
Advantages of AUC
- Detection of samples in solution, with limited buffer constraints.
- No column matrix.
- Simple method that can assess large concentration and particle size ranges, through modulation of wavelengths, centerpieces, and rotor speeds.
- Sample recovery.
- Dye free technique.
- Limited sample preparation.
Additional methods for antibody characterization
For high-throughput antibody characterization, Beckman Coulter Life Sciences offers straightforward assays to determine IgG titer or protein aggregation. The Valita Titer assay is a plate-based method to quantify IgG titer. It is available in 96- or 384-well plates and offers an easy, fast and high-throughput solution to measure antibody concentration in less than 15 minutes and in only three steps. As an additional benefit, this tool can be easily automated with the Biomek i-Series Automated Workstation.
An alternative method for antibody aggregation screening is the Valita Aggregation Pure assay. This assay comes in 96-well plates and enables high-throughput aggregation screening in less than 15 minutes. The simple workflow of adding the sample, incubating and measuring the results in a plate reader can be easily automated.
Learn more about our products:
Not intended or validated for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions.
References
- Harding SE. Analytical Ultracentrifugation as a Matrix-Free Probe for the Study of Kinase Related Cellular and Bacterial Membrane Proteins and Glycans. Molecules. 2021 Oct 8;26(19). PMCID: PMC8512968
- Chaturvedi SK, Parupudi A, Juul-Madsen K, Nguyen A, Vorup-Jensen T, Dragulin-Otto S, Zhao H, Esfandiary R, Schuck P. Measuring aggregates, self-association, and weak interactions in concentrated therapeutic antibody solutions. MAbs. 2020 Dec;12(1):1810488. PMCID: PMC7531506
- Bou-Assaf GM, Budyak IL, Brenowitz M, Day ES, Hayes D, Hill J, Majumdar R, Ringhieri P, Schuck P, Lin JC. Best practices for aggregate quantitation of antibody therapeutics by sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation. J Pharm Sci. 2022 Jul;111(7):2121–2133. PMCID: PMC9232890
- Clardy SM, Lee DH, Schuck P. Determining the Stoichiometry of a Protein-Polymer Conjugate Using Multisignal Sedimentation Velocity Analytical Ultracentrifugation. Bioconjug Chem. 2021 May 19;32(5):942–949. PMID: 33848127
Valita, Valita Titer, Valita Aggregation Pure and the ValitaCell logo are trademarks of ValitaCell Ltd in the United States and other countries. ValitaCell is a Beckman Coulter Company.
Related Content
Talk to an Expert on Analytical Ultracentrifugation
We are here to help, please reach out anytime