基于纯物理学原理
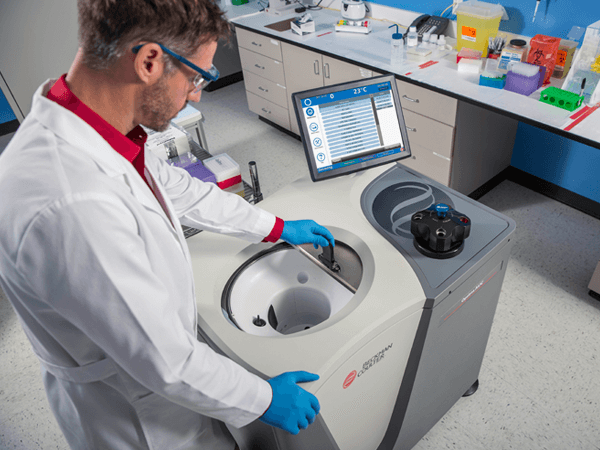
分析型超速离心技术(AUC)是表征生物大分子特性、研究生物分子理化特性的主要技术手段之一。通过对样品施加高离心力, Optima AUC 可精准测定蛋白质、核酸、病毒及其他粒子在天然状态下的流体力学和热力学特性,提供分子量、大小分布、形状和分子之间相互作用的重要信息,是生物化学、分子生物学和纳米技术等领域不可或缺的重要工具。
联系我们
寻求真理的前沿技术
无论是研究蛋白质、核酸、聚合物、病毒样颗粒还是纳米颗粒, Optima AUC
都能提供无与伦比的灵活性和精准度,精准检测和表征随生物或环境变化(如 pH 值和温度)的大分子寡聚状态、异质性和构象变化等相关信息。分析型超速离心技术(AUC)具备卓越灵活性,支持更广泛的浓度检测范围,兼容多种溶剂类型,实现从微小肽段到大病毒颗粒的精准测量。
Optima AUC 在确定大分子的化学计量、分子量和大小,以及深入剖析分子间可逆与不可逆的相互作用方面发挥着至关重要的作用。此外,AUC 在区分颗粒负载率方面展现出独特优势,是分子生物学和生物化学领域不可或缺的关键工具。
了解 AUC 如何精准表征大分子并加速您的研究进程。
全能型仪器:集多种实验方法于一身
分析型超速离心技术是一种应用广泛且提供丰富信息的技术,能够精确测定生物相关条件下天然状态大分子的关键特性,如大小、形状、化学计量以及结合特性等,这些优势令其他正交分析技术难以企及。
Optima AUC 搭载两个无缝集成的光学检测系统:紫外/ 可见光(UV/Vis)检测系统,用于检测溶液中 190-800 nm 紫外可见光吸收分析物;瑞利(Rayleigh)干涉光学检测系统,用于监测和检测样品和参比溶液间存在差异的任何分析物。

实验方法
AUC 凭借多样化的正交方法,展现出了广泛的应用前景,支持研究人员基于特定需求灵活定制实验,跨不同应用和更广泛的浓度范围轻松获得精准的检测结果。
AUC 主要实验方法包括:沉降速率(SV)法,可提供分子大小和形状的高分辨率流体动力学信息;沉降平衡(SE)法,可提供溶液热力学信息,包括准确的摩尔质量;以及密度梯度平衡(DGE)法,可根据颗粒在密度梯度内的浮力密度分离颗粒,减少常规样品量需求。
此外,Optima AUC的创新功能,即多波长 AUC,可在 SV 和 DGE 实验中提取分析物的光谱特性,帮助用户深入探究分子间相互作用信息。点击以下链接,详细了解上述实验方法及其如何助您加速研究进程。
相关资料
联系我们了解更多关于AUC分析型超速离心机