Enumeration of T, B, and NK Subpopulations in Aged Whole Blood Samples
Violetta Headley1, Xiangyang Dong1, Raquel Cabana1, Veronica Trujillo1, Michael Thomas2, Robert Magari3, Elena Afonina1
1Clinical Application Development, Life Sciences, Beckman Coulter, Inc.
2Research, Life Sciences Beckman Coulter, Inc.
3Clinical Affairs, Diagnostics, Beckman Coulter, Inc.
Introduction
The use of flow cytometric analysis of peripheral whole blood to enumerate lymphocyte subsets is commonly used to assess the immunological status of patients in a wide variety of clinical conditions. The testing to enumerate lymphocyte subsets often occurs in specialized reference laboratories remote from the site of blood collection from the patient, which can cause delays between specimen collection and performance of the assay. In addition, once the lab has prepared the specimen for flow cytometry analysis, it is not uncommon for the lab to store this prepared sample prior to analysis or reanalysis. Previous studies have shown that the scatter and fluorescence properties of various cell subsets of whole blood stored in EDTA change as a specimen or prepared sample ages. The general observations regarding specimen age have been that the relative proportion of T-cells increases, while the number of detectable B-cells decreases (Nicholson, et. al 1993, Ekong, et al 1993, Jalla, et. al. 2004). In this study we demonstrate that the new AQUIOS-Tetra method developed for the enumeration of T, B and NK lymphocyte subsets provides accurate results for specimens stored in EDTA for up to 24 hours post venipuncture at room temperature.
Specimen Age and Prepared Sample Stability Analysis Method
The AQUIOS CL instrument with Tetra application is an integrated system of sample preparation and sample analysis; it analyzes samples within 3 minutes after the lysing reagent is added to the sample stained with antibodies. The software controls sample preparation and analysis to limit the overlysing impact. In this study, the whole blood samples were tested at 24 hours of post venipuncture and after a 3 minute incubation time as prepared samples. Each specimen was tested in duplicate at each time point.
Table 1. Time Points for each specimen
NOTE: The results from at least three time points testing were required to perform regression analysis.
Seventy-three (73) specimens, including normal and clinical (HIV+) donors were tested for data analysis. The drift (change) in absolute count and percent positive for CD3+, CD3+/CD4+, CD3+/CD8+, CD3-/ CD19+ and CD3-/ CD56+16+ lymphocyte subsets for all replicates were assessed between the reference point 0-0 and other time points (24-0, 24-3). A 95% confidence limit of the drift was also calculated.
AQUIOS drift analysis for Specimen Age
Data was modeled as a linear function of specimen using a mixed model including all the data collection at each time point (0-0, 24-0, and 32-0). Samples constituted the random component of the model while “age” was used as a linear regression fixed effect. The PROC MIXED routine of SAS 9.3 was used for data analysis.
Drift (δAge) at a certain time point was calculated as the difference between the response at that time point and the response at time zero (t0).
AQUIOS drift analysis for Prepared Sample
Drift of prepared samples (δPrepared) was calculated as the difference between the average response of samples aged for 24 hours and prepared for three minutes (24-3) and the average response of samples aged 24 hours tested immediately (24-0). δPrepared = X24hrs + 3 min – X24hrs, where X24hrs + 3 min and X24hrs were the respective averages. Standard error of this drift (σPrepared) was calculated as the standard error of the difference between these two time points.
AQUIOS total drift analysis
Drift at stability claim (24 hours aged and 3 minutes prepared) was calculated as the sum of the specimen age component and the prepared sample component as: δTotal = δAge + δPrepared. The confidence limits of the drift were calculated based on the standard error of the drift and 95% confidence.
Specimen Age and Prepared Sample Data Analysis Results
Table 2. Mean values of the recovered drift at each time point
Table 3. Specimen and Prepared Sample Stability Results
Conclusions
Based on this study, the AQUIOS CL instrument with Tetra application provides accurate results for recovery of the T, B and NK lymphocyte subsets in clinical and normal specimens collected into the EDTA K3 tubes when stored at room temperature for up to 24 hours.
AQUIOS CL is a Class I Laser Product
Purity and recovery are important in the calculation of percentages and absolute counts of lymphocyte subsets. Fill the form to download our gating strategy for Tetra reagents.

HIV Advanced Disease Management

HIV Advanced Disease Management Solutions
Monitoring CD4 lymphocyte counts is essential in providing critical information that impacts patient care. CD4 monitoring allows caregivers to know when the disease transforms and stage its progression so they can implement the most appropriate intervention..
Fast Throughput Subset Analysis with AQUIOS CL
In the clinical management of immune deficiency diseases, accurately counting the absolute cell numbers of leukocyte subsets and measuring the percentage of individual subtypes in blood is critical.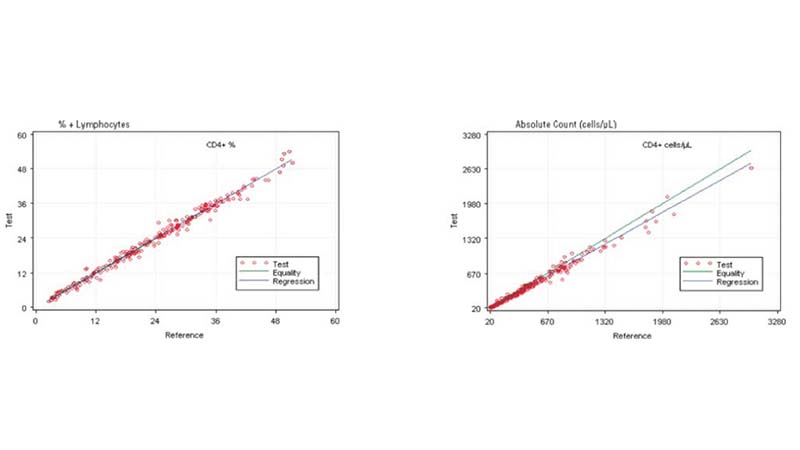
Comparing the AQUIOS CL PLG Application to the FC500 MCL FlowCARE PLG Application
Based on this study, the data suggests a strong correlation between the AQUIOS CL PLG application and the FC500 MCL FlowCARE PLG application.
AQUIOS CL Tetra and Aged Whole Blood samples
Based on this study, the AQUIOS CL instrument with Tetra application provides accurate results for recovery of the T, B and NK lymphocyte subsets in clinical and normal specimens collected into the EDTA K3 tubes when stored at room temperature for up to 24 hours.Error Prevention on AQUIOS CL overview
Laboratory standards and regulations set forth by governmental bodies such as the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) help to define the procedures that laboratories follow
Error prevention during Startup and Worklist creation
The AQUIOS CL system employs several features that work to prevent errors during startup, cleaning, and worklist generation, including Autocleaning, Test Requests to and from the LIS and Creating Worklists.
Error Prevention During Sample Prep
The AQUIOS CL system employs several features that work to prevent errors during sample prep.