Automated Cord Blood Cell Viability and Concentration Measurements Using the Vi‑CELL XR
Introduction

Stem cells, due to their differentiation into mature blood cells, are the key to successful bone marrow transplantation research. More recently, it has been found that umbilical cord blood is also a plentiful and rich source of hematopoietic stem cells.(1) Thus, both bone marrow and cord blood are used in treatment research of numerous cancers, immunological disorders, and certain genetic diseases.
Currently, many facilities provide parents the option to store, or bank, their newborn baby’s cord blood.(2) When cells are banked—usually in liquid nitrogen—two parameters must be accurately assayed. These measurements are cell concentration and percentage of cell viability.(3) These measurements are performed prior to storage and after the thawing process. Cells may decrease in both number and viability, mainly due to the cryopreservative employed in the freezing process (usually DMSO).
The Vi-CELL XR (Figure 1) automates the manual trypan blue vital dye exclusion method for cell viability determinations. In addition, the instrument provides an objective measurement of cellular concentration. As mentioned, these are two critical parameters required in the cord blood cell banking process. The objective of this work was to describe a method for cord blood sample preparation, and develop a cell type, accurate set of instrument parameters, for the Vi-CELL XR.
Materials and Methods
A sample of cord blood was obtained from Baptist Hospital, Miami, FL, by the SAS laboratory at Beckman Coulter. The blood was diluted 1:1 using room-temperature phosphate buffered saline. The standard Ficoll* gradient separation method was used to isolate the mononuclear cells.(4) Isolated cells were washed once in PBS and resuspended in 2 mL of Isoflow* (Isoton* II). A 1:10 dilution of the cell suspension was prepared by placing 100 µL of cells into 900 µL of Isoflow in a standard Vi-CELL™ sample cup. The Vi-CELL XR was used to develop the cord blood cell type. Prior to sample analysis, the Vi-CELL™ concentration control was assayed.Results
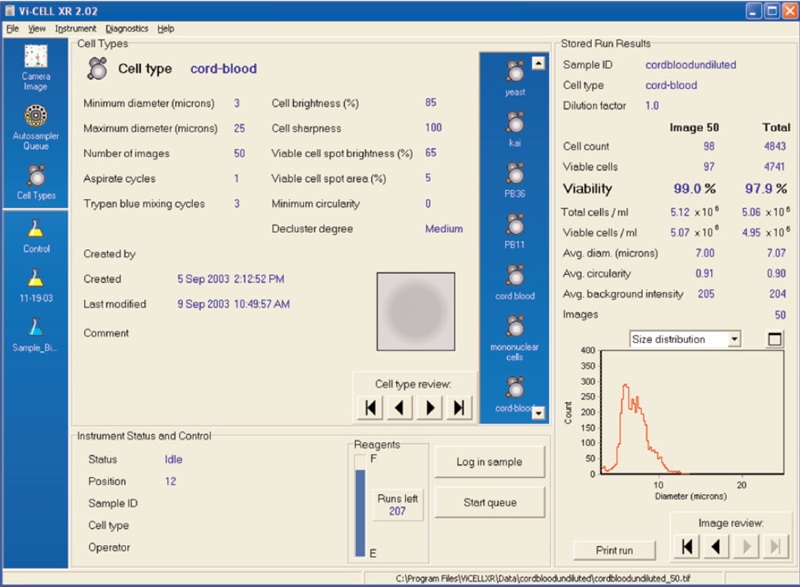
Figure 2 shows the results of the Vi-CELL concentration control. Figure 3 illustrates a cord blood cell image on the Vi-CELL XR. Figure 4 shows the cell type parameters used to analyze cord blood cells. The size range was set from 3 to 25 microns. Cell brightness: 85; cell sharpness: 100; viable cell spot brightness: 65; viable cell spot area: 5.Conclusions
Cord blood stem cell infusions have significant advantages over bone marrow transplants. Viability and concentration of cord blood cells may be assayed using the Vi-CELL XR . The cell type settings for cord blood samples were determined. Size range 3 to 25 microns. Imaging parameters: Cell brightness: 85; cell sharpness: 100; viable cell spot brightness: 65; viable cell spot area: 5.
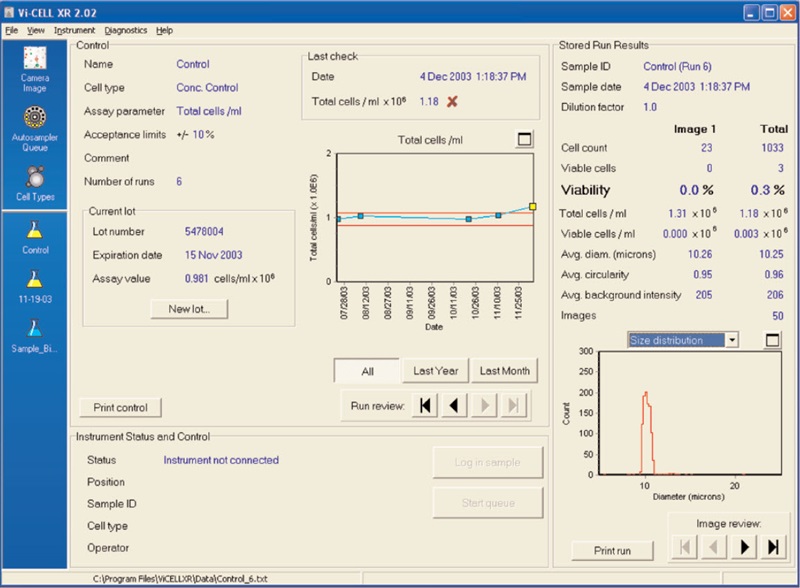
Figure 2. Results of the Vi-CELL concentration control.
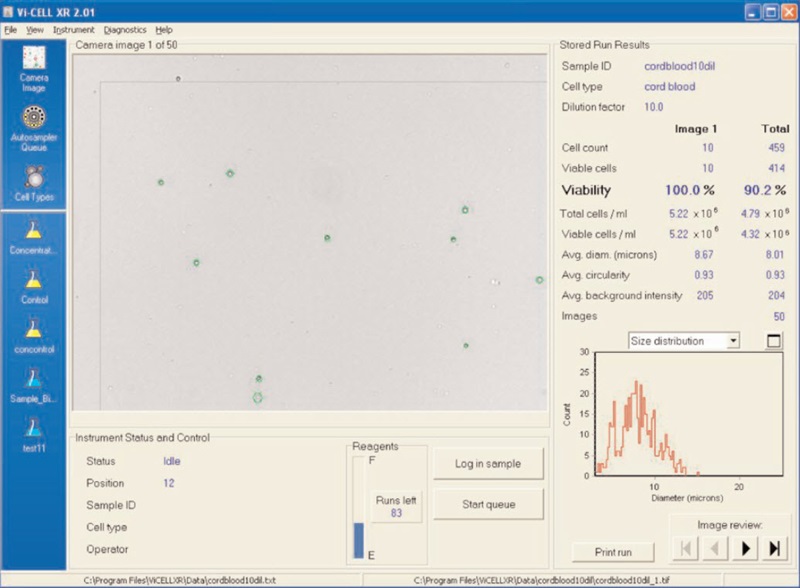
Figure 3. A cord blood cell image on the Vi-CELL™ XR.
References
- Kurtzberg, J., Laughlin, M., Graham, M. L., et al. Placental blood as a source of hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. Blood 90, 4665-4678 (1997).
- American Academy of Pediatrics Work Group on Cord Blood Banking. Cord blood banking for potential future transplantation: subject review. Pediatrics, Vol. 104, No. 11, 116- 118 (1999).
- Fiorino, Susan, Johns Hopkins University, The Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center. Personal Communication.
- Boyum, A. Separation of white blood cells, Nature 204, 793-794 (1964).
Helpful Links
-
细胞计数和活率分析仪
-
Vi-CELL BLU 细胞计数和活率分析仪
- 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance with the Vi-CELL BLU Cell Viability Analyzer
- Vi-CELL BLU 细胞计数和活率分析仪与 Sartorius Ambr® 250 高通量生物反应器及 Ambr® 15 细胞培养系统整合解决方案
- Vi-CELL BLU 自动细胞计数和细胞活率分析仪自动化整合
- Automated Bioreactor Sample Delivery to the Vi-CELL BLU Cell Viability Analyzer
- 样品从生物反应器到Vi-CELL BLU 细胞活率分析仪的自动化输送
- 虚拟产品演示请求
- Vi-CELL BLU Webinars
- Vi-CELL BLU与Vi-CELL XR的比较
- VI-CELL BLU 细胞计数和活率分析仪特点
- VI-CELL BLU细胞计数和活率分析仪软件
- 细胞识别参数设置指南和优化
- Vi-CELL BLU 虚拟演示视频库
- Vi-CELL MetaFLEX 高速细胞培养生化分析仪
- Vi-CELL XR 细胞计数及活率分析仪
- Multisizer 4e 库尔特颗粒计数及粒度分析仪
- Z 系列库尔特计数仪
- Multisizer 3 库尔特颗粒计数及粒度分析仪
-
Vi-CELL BLU 细胞计数和活率分析仪
-
资源中心
- 研究领域
- 细胞类型
- 疾病管理
- 生物制剂发现和开发
- 疾病研究
- 行业领域
-
行业标准与法规要求
- USP<643>
- IVDR 2022 is a marathon, not a sprint. We’ll help you go the distance.
- 21 CFR Part 11 - Data Integrity
- Maintaining Data Integrity: Understanding FDA ALCOA Guidance
- European Pharmacopoeia EP 2.2.44
- EU GMP Annex 1
- EU GMP Annex 11
- ICH Q2
- ISO 21501
- ISO Regulations
- IVD-Regulation (IVDR)
- Regulatory Entities: Separation with Cooperation
- USP 1046
- USP 1047
- USP <788>, <787> and EP2.9.19
- USP <790>
- ISO 11171
- ISO 14644-1
- USP 787
- Methods
- 探索更多资源,丰富您的样本类型
-
技术介绍
- Machine Learning Assisted Analysis for Cytometry Data
- 激光衍射
- NGS测序文库制备
- Analytical Ultracentrifugation
- Dynamic Light Scatter
- 干粉试剂技术
- Accessible Flow
- Acoustic Sample Management
- Elevating Bioprocessing Efficiency with Avanti JXN and Optima XPN Centrifuges
- How the Vi-CELL BLU Analyzer supports You from Data to Insights
- 实验室自动化原理
- 离心技术
- Cytobank Training
- Flow Cytometry
- SPRI Beads
- Accessible Flow Learning Center
- 流式细胞术基础知识
- Flow Cytometry Data Reproducibility
- Flow Cytometry Panel Design
- 库尔特原理
- 阅读材料
- 视频
- 应用
- 实验方法
- 研究领域

